
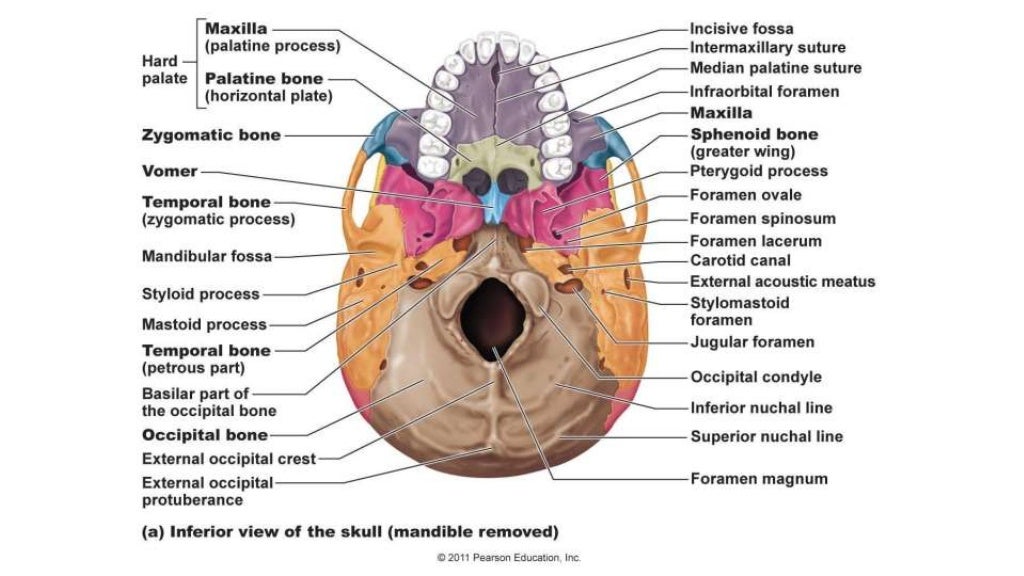
The flat bones are made up of varying thickness of spongy bone between two layers of compact bone. They are plate like, affording large surface area for the attachment of muscles and protection of subjacent structures. Flat bonesįlat bones are expanded in two directions. Some bones though long they do not have a medullary cavity and are sometimes referred to as elongated bones. Example is Ribs. Some long bones do not develop completely and their medullary cavity is very small or even absent which are called as aborted long bones. Examples like ulna of horse. Long bones are found in the limbs and act as pillars for support and as levers. The spaces in the cancellated bone of the epiphyses are occupied by red marrow. Inside of the compact bone, there is a thin layer of spongy bone lining the medullary cavity.Įach epiphysis consists of spongy bone covered by a thin layer of compact bone. The wall consists of dense compact bone of considerable thickness in the middle part of the shaft but becoming thinner towards the extremities.
The shaft encloses the medullary cavity, which in life is occupied by yellow marrow. Long bones have an elongated cylindrical part, the shaft or diaphysis and two expanded extremities or epiphysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
